Types of Biology
The Greek words bios and logos are the origins of the term “biology”. Bios means life and logos means study. So, biology is the science which studies life and alive organisms. An organism means an alive entity having one cell such as bacteria, or several cells such as plants, fungi, and animals. Biology studies these living organisms’ chemical processes, physical structure, physiological mechanisms, molecular interactions, evolution, and development. Biological science may seem very complex but some specific unifying concepts combine it into a single, consistent field. Biology specifies the cell as life’s basic unit, genes as heredity’s basic unit, and evolution as the generator that drives the species’ creation and extinction.
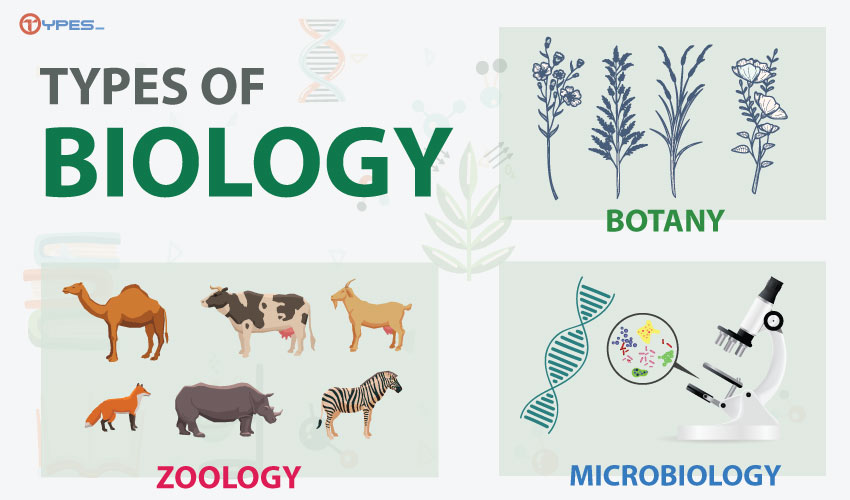
There are mainly three types of biology
- Zoology
- Botany and
- Microbiology
Apart from the above ones, there are many other branches of biology. The mentionable branches or types among them are given below:
|
|
|
|
1. Zoology:
Zoology scientifically studies various aspects such as structure, behavior, classification, distribution, and physiology of animals. Aristotle is called the “father of Zoology”. Animal science is another name of zoology.
Zoology is descriptive as well as analytical. It is basic science and at the same time, is an applied science. A basic zoologist is only concerned with the knowledge of animals but not with the application of the gained knowledge. An applied zoologist is concerned with the information which will directly help animals and humans (e.g. medicine).
2. Botany:
Botany deals with the scientific study of various aspects of plants such as their structure, physiology, ecology, and genetics. Theophrastus is called the “father of Botany”. Plant science is another name of botany.
Botany researches can be divided into different categories depending on which subcategory of biology the research is based on. For instance, botanists can study plant genetics, plant anatomy, ecology, cytology, biophysics, biochemistry, physiology, plant taxonomy, molecular biology, microbiology, and paleobotany. Botanists can also study on a particular type of plants such as bryology (the study of mossesli), lichenology (the study of lichens), mycology (the study of fungi), pteridology (the study of ferns), and phycology (the study of algae). Applied botany includes agronomy, forestry, food science, horticulture (production of ornamental crops and plants), plant breeding, natural resource management, and plant pathology.
3. Microbiology:
Microbiology studies various aspects of microscopic organisms. These microscopic organisms can be acellular, multicellular, or unicellular. Leeuwenhoek is called the “father of Microbiology”.
Other Branches or Types of Biology
Taxonomy: Taxonomy discusses the nomenclature, identification, and classification of living organisms.
Anatomy: Anatomy studies the internal structure of organisms that can be seen with eyes after dissection.
Morphology: Morphology deals with the study of the size, external forms, color, shape, relative position, and structure of the different living organs of alive beings.
Cytology: Cytology focuses on the structure and form of cells and also the activities of the nucleus and additional organelles.
Histology: Histology studies the structure and organization of tissues as seen through a light microscope.
Molecular Biology: Molecular biology deals with the study of the structure, nature, function, physicochemical organization, interaction, and synthesis working of bio-molecules. These biomolecules bring about and command different functions of the protoplasm.
Cell Biology: Cell biology discusses the organizational, morphological, physiological, biochemical, pathological, genetic, evolutionary, and developmental aspects of cell and its elements.
Embryology: Embryology studies the fertilization, division, differentiation, and growth of the zygote into an embryo. In other words, it discusses the early development of alive organisms before the achievement of the size and structure of the offspring.
Physiology: Physiology focuses on the normal functions and processes of living beings and their body parts.
Genetics: This type or branch of biology studies genes, heredity, and genetic variation in alive organisms. Heredity discusses the expression and transmission of qualities from parents to children or offspring.
Ecology: Ecology discusses the relations of living organisms to one another and the environment.
Evolution/Evolutionary Biology: Evolution or evolutionary biology discusses life’s origin and new forms of the organism from the previous types by modifications including adaptations and changes.
Eugenics: Eugenics is a form of biology dealing with aspects related to impairment or improvement of the race, particularly that of humans.
Exobiology: Exobiology scientifically enquires life’s possibility in the outer space.
Paleontology: Paleontology studies the impressions and remains of past organisms available in the rocks of various ages. More precisely, it studies fossils.
Virology: Virology is the type or branch of biology that studies viruses and their every aspect.
Immunology: Immunology is a branch of medicine and biology which deals with immunity.
Marine Biology: Marine biology scientifically studies the organisms living in the ocean. It studies the ocean ecosystems.
Mycology: Mycology scientifically focuses on fungi.
Photobiology: Photobiology scientifically discusses the interactions of living organisms and light.
Parasitology: Parasitology is the branch or type of medicine or biology which is focused on parasitic organisms.
Biophysics: Biophysics applies the laws of physics to the learning of biological phenomena or living organisms.
Biochemistry: Biochemistry applies chemistry to the learning of living organisms. It is the branch or type of biology that deals with the physicochemical and chemical processes occurring within living beings.
Biotechnology: Biotechnology is the application of biological processes e.g. micro-organisms’ genetic manipulation for the production of hormones, antibiotics, etc.
Structural Biology: Structural biology is a type or branch of molecular biophysics, biochemistry, and biology. It discusses biological macromolecules’ molecular structure.
Radiobiology: Radiobiology studies ionizing radiation’s action on living organisms.
Theoretical Biology: Theoretical biology is also known as mathematical biology. It is a field of scientific research that uses a range of mathematical applications in medicine, biology, and biotechnology.

